New ARM product reduces risk of high interest rates
New ARM product reduces risk of high interest rates
f you remember the housing crash back in 2008, you may recall just how popular adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) were back then. And after years of being virtually nonexistent, more people are once again using ARMs when buying a home. Let’s break down why that’s happening and why this isn’t cause for concern.
Why ARMs Have Gained Popularity More Recently
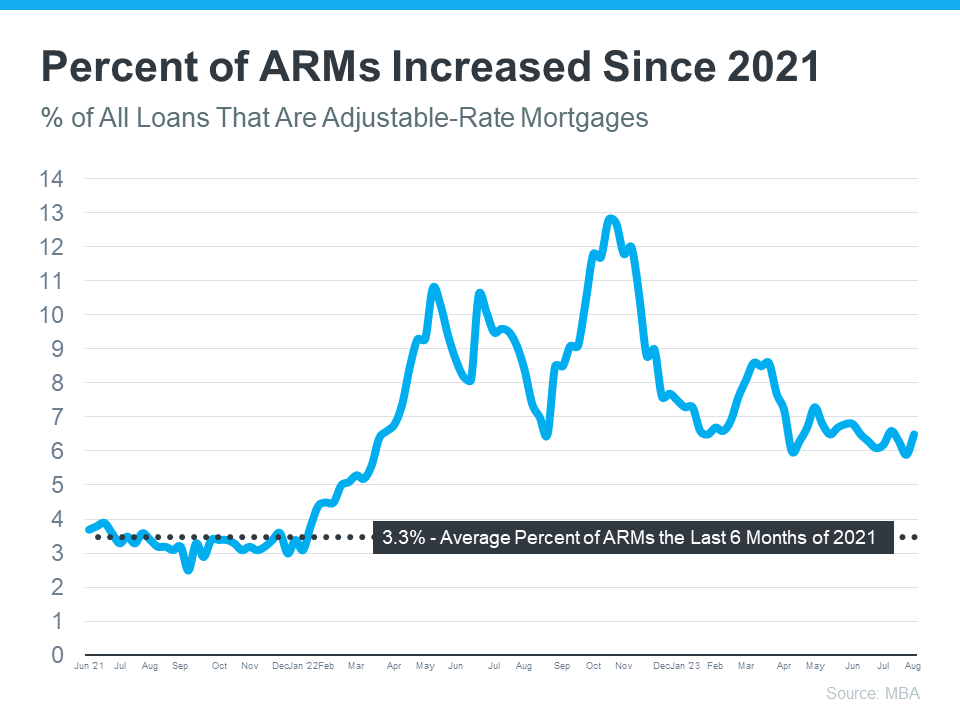
This graph uses data from the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) to show how the percentage of adjustable-rate mortgages has increased over the past few years:
As the graph conveys, after hovering around 3% of all mortgages in 2021, many more homeowners turned to adjustable-rate mortgages again last year. There’s a simple explanation for that increase. Last year is when mortgage rates climbed dramatically. With higher borrowing costs, some homeowners decided to take out this type of loan because traditional borrowing costs were high, and an ARM gave them a lower rate.
Why Today’s ARMs Aren’t Like the Ones in 2008
To put things into perspective, let’s remember these aren’t like the ARMs that became popular leading up to 2008. Part of what caused the housing crash was loose lending standards. Back then, when a buyer got an ARM, banks and lenders didn’t require proof of their employment, assets, income, etc. Basically, people were getting loans that they shouldn’t have been awarded. This set many homeowners up for trouble because they couldn’t pay back the loans that they never had to qualify for in the first place.
This time around, lending standards are different. Banks and lenders learned from the crash, and now they verify income, assets, employment, and more. This means today’s buyers actually have to qualify for their loans and show they’ll be able to repay them.
Archana Pradhan, Economist at CoreLogic, explains the difference between then and now:
“Around 60% of Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARM) that were originated in 2007 were low- or no-documentation loans . . . Similarly, in 2005, 29% of ARM borrowers had credit scores below 640 . . . Currently, almost all conventional loans, including both ARMs and Fixed-Rate Mortgages, require full documentation, are amortized, and are made to borrowers with credit scores above 640.”
In simple terms, Laurie Goodman at Urban Institute helps drive this point home by saying:
“Today’s Adjustable-Rate Mortgages are no riskier than other mortgage products and their lower monthly payments could increase access to homeownership for more potential buyers.”
Bottom Line
If you’re worried today’s adjustable-rate mortgages are like the ones from the housing crash, rest assured, things are different this time.
And, if you’re a first-time homebuyer and you’d like to learn more about lending options that could help you overcome today’s affordability challenges, reach out to a trusted lender.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
According to The New York Times:
In August, the New York Mortgage Company began marketing an ARM that offers borrowers long-term protection against interest-rate increases, while still allowing them to benefit from decreases.
The company’s Homeowner Protection ARM is a 30-year loan with an interest rate that starts at 6.5 percent, then resets monthly according to the London Interbank Offered Rate [the LIBOR rate, as it is commonly known as], a short-term interest-rate index.
But unlike most ARM’s, whose interest rates can rise to a maximum of about 13 percent, the Homeowner Protection ARM has a maximum annual percentage rate of about 7 percent for the first 10 years.
Should the London Interbank index drop, though, the interest rate on the loan would do the same, down to a floor of 4 percent. After 10 years, the interest rate ceiling would rise to 10 percent.
There are several advantages to an adjustable rate mortgage loan such as this. First, the adjustable rate may be lower than the current fixed rate, of course. Second, the loan cannot increase in rate as high as other ARMs, at least that’s what they say.
Third, because there are limits on how high the loan can reset, even after 10 years, you are much less likely to refinance.
The trouble with ARMs today is, you might get a good rate, but, three or five years from now, rates may have gone up. If so, you’ll probably want to refinance into a fixed rate loan, and the closing costs, etc., of doing that will eat up a lot of the money you’ve saved from having an ARM. With these new ARM loans, you’ll most likely stay in them, longer, or forever, allowing you to keep the savings.
Ask your mortgage loan professional.
Sorry we are experiencing system issues. Please try again.
Click Here: Back to Boston Real Estate Home Search
Buying a Boston Real Estate for sale
- Tips on buying a Boston real estate
- Boston real estate buyers how to beat all cash offers
- 5 tips on buying a Boston real estate for sale
- Benefits of buying a Boston real estrate condo
- Design tips for Beacon Hill condo buyers
- Boston Beacon Hill condos for sale 5 must know terms
- The difference between a Beacon Hill condos and a Beacon Hill loft
- Common mistakes when buying a Beacon Hill condo
- Buying a Beacon Hill condo with kids
- Is it time to ditch my Beacon Hill condo agent?
- Beacon Hill condos for sale: Do I need 20% down?
- 3 signs you’re going to buy a Boston Beacon Hill condo
- 6 principles to know when buying a Beacon Hill condo
- How to select a Boston Beacon Hill condo agent
- Boston Beacon Hill condos for sale downpayment
- Boston Beacon Hill condos finance
- Beacon Hill condos for sale what is negotiable
- Beacon Hill condos for sale: What it take to get a mortgage.
- Boston Beacon Hill condos for sale. Understand the condo association
- How much do Boston Beacon Hill condos cost?
- How to select a Boston real estate broker
- Beacon Hill condos for sale: Clutter Free
- Beacon Hill condos for sale:Security Tips
- Beacon Hill condo renters are misinformed
- Boston Beacon Hill condos for sale: Design trends
- Boston Boston real estae: Fixer up
- 8 Beacon Hill condo designs
- How to sell your Midtown condo using social media
- Boston Boston real estate sales volume
- Wage increases make Boston real estate less or more affordable
- Boston Boston condos the importance of high owner occupancy
- Why you should buy a Boston real estate off season
- The definitions of Boston real estate terms and what they mean?
- UPDATED 2023 Boston Real Estate Blog